The Power of Google Analytics Secondary Dimension: Making Best Use Of Insights
Opening the Power of Secondary Measurement Analytics for Boosted Data Insights and Decision-Making
In the realm of data analytics, main measurements frequently take the limelight, yet truth depth of insights lies within the realm of additional measurements. These added information factors provide a nuanced point of view that can illuminate partnerships and patterns not conveniently apparent at very first look. By harnessing the power of secondary dimension analytics, organizations can unveil covert patterns, discover connections, and essence much more significant final thoughts from their data. The capacity for enhanced decision-making through the utilization of these secondary dimensions is substantial, assuring a much deeper understanding of intricate information sets and leading the way for more enlightened critical selections.
Value of Secondary Measurements
Checking out the importance of secondary measurements in analytics unveils the hidden layers of information insights critical for notified decision-making in various domain names. Additional measurements supply a deeper understanding of key data by offering extra context and perspectives. By including additional measurements into analytics, companies can draw out more nuanced and detailed understandings from their datasets.
One key relevance of additional measurements is their ability to sector and categorize main data, permitting a much more thorough analysis of details subsets within a dataset. This division makes it possible for companies to recognize patterns, patterns, and outliers that could not appear when considering the data all at once. Second dimensions help in discovering connections and dependences in between various variables, leading to more accurate forecasting and predictive modeling - secondary dimension.
Moreover, second measurements play an important function in boosting information visualization and coverage. By including second measurements to visualizations, such as graphes or graphs, analysts can create more informative and interesting depictions of information, promoting far better interaction of searchings for to stakeholders. On the whole, the assimilation of secondary measurements in analytics contributes in opening the full potential of data and driving evidence-based decision-making.
Secret Benefits of Utilizing Secondary Dimensions
Utilizing second measurements in analytics uses organizations a tactical advantage by augmenting the deepness and granularity of information insights. One essential benefit of including second measurements is the capability to segment and filter information, enabling a much more detailed evaluation of certain elements within a dataset. This segmentation makes it possible for companies to acquire a more nuanced understanding of their target market, performance metrics, and various other critical information points. By studying information utilizing secondary measurements such as time, place, device kind, or individual demographics, companies can discover patterns, trends, and relationships that may or else stay hidden.
In addition, the usage of second dimensions improves the context in which key data is translated. It provides a much more thorough view of the connections in between different variables, allowing companies to make educated choices based upon a more alternative understanding of their information. Additionally, additional measurements facilitate the identification of outliers, abnormalities, and locations for optimization, ultimately resulting in a lot more effective techniques and enhanced end results. By leveraging secondary dimensions in analytics, organizations can harness the complete possibility of their information to drive far better decision-making and achieve their company goals.
Advanced Data Analysis Techniques
A deep study sophisticated data evaluation methods exposes innovative approaches for removing beneficial understandings from complex datasets. One such technique is artificial intelligence, where algorithms are utilized to determine patterns within data, predict outcomes, and make data-driven choices. This approach permits the automation of imp source logical design building, enabling the handling of huge quantities of data at a faster pace than traditional techniques.
An additional innovative strategy is predictive analytics, which makes use of analytical formulas and machine discovering strategies to forecast future outcomes based upon historical data. By analyzing fads and patterns, organizations can anticipate customer habits, market trends, and possible dangers, empowering them to make proactive choices.
In addition, message mining and belief analysis are beneficial strategies for drawing out insights from disorganized data sources such as social networks remarks, client evaluations, and survey feedbacks. By assessing text information, companies can understand client point of views, identify arising patterns, and boost their services or items based on responses.
Enhancing Decision-Making With Secondary Measurements
Enhancing decision-making via second dimensions makes it possible for organizations to make more informed and targeted calculated options. By segmenting customer data based on second measurements like purchasing background or involvement levels, firms can tailor their advertising and marketing methods to certain target market sectors, leading to enhanced conversion prices and client fulfillment. Furthermore, secondary measurements can help determine connections and connections between various variables, making it possible for organizations to make data-driven decisions that drive growth and earnings.
Applying Additional Dimension Analytics
When integrating secondary measurements in analytics, organizations can open deeper insights that drive strategic decision-making and improve total performance. This requires comprehending the details questions the company seeks to respond to and the information points called for to address them.
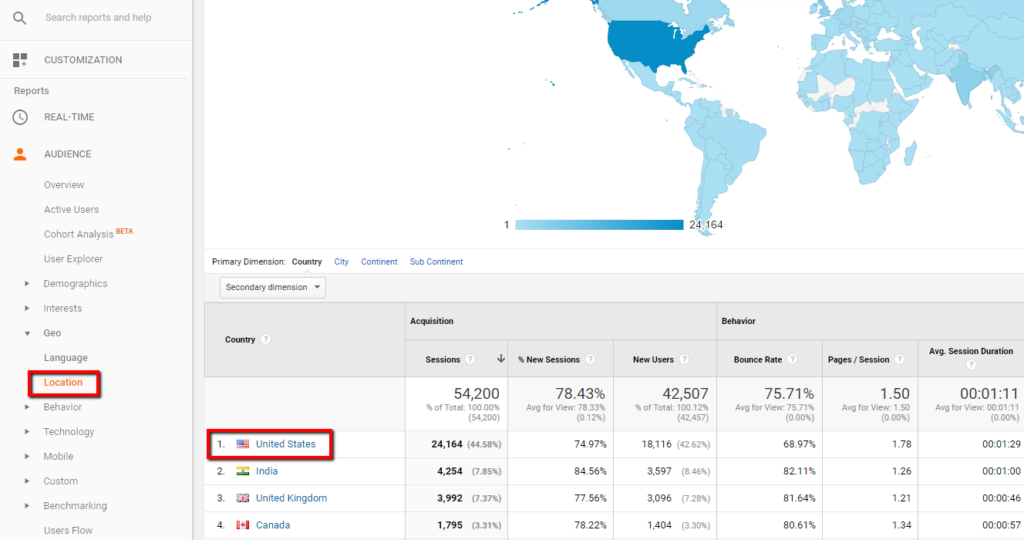
In addition, organizations must utilize advanced analytics tools and modern technologies to streamline the process of including second dimensions. These tools can automate information handling, analysis, and visualization, allowing companies to concentrate on analyzing insights instead of hands-on information adjustment.
Conclusion
In final thought, second measurement analytics play an essential function in improving information understandings and decision-making procedures. By utilizing advanced data analysis techniques and carrying out second measurements properly, companies can open the power of their information to drive strategic business decisions. The essential benefits of utilizing additional Get More Info dimensions can not be overstated, as they offer a deeper understanding of data trends and relationships. It is important for organizations to leverage secondary why not look here dimension analytics to stay affordable in today's data-driven landscape.
In the realm of information analytics, primary measurements usually take the spotlight, yet the true depth of insights exists within the world of additional dimensions.Making use of additional dimensions in analytics offers companies a calculated advantage by augmenting the deepness and granularity of data insights. By leveraging second dimensions in analytics, companies can harness the full potential of their information to drive better decision-making and attain their service objectives.
Applying information validation procedures and routine audits can help preserve data top quality and dependability.
By making use of sophisticated information analysis strategies and carrying out secondary dimensions effectively, organizations can open the power of their information to drive critical service choices.